About Water – Filtration and Purification Techniques
As our most precious resource, water is becoming more and more contamination through man-made pollution, the increase, and severity of the disease, an increase in the ozone layer, deforestation of rain forests. This is evident through the rapid yearly increase in waterborne illness and diseases. Our scientists are working on ways to reverse this cycle through technologies and processes.
To help us understand what is available this section of the web is dedicated to an introduction to water and technologies available for water filtration and or purification
Did you know their is about 5.5 trillion macro and microplastic pieces in out our seas. About 8 million plastic bottles get washed into our oceans each DAY!!

Water Technology Principals
There are a large number of different technologies that can be employed to filter, sterilize, and purify water to make it palatable and safe to drink. Many of these technologies have been around for many years. New technologies and processes are continually being introduced to enhance the quality of water. With pollution, population growth, deforestation, and growing.
Here are some of the mainstream filtration, sterilization, and purification processes;population, water contamination is becoming an increasing problem across the globe.
Here are some of the mainstream filtration, sterilization, and purification processes;
- Micro-Filtration
- Nano Filtration
- Electrochemical
- Iodine Disinfection
- Chlorine Disinfection
- Chlorine Dioxide Disinfection
- Ultra Violet light
- Reverse Osmosis
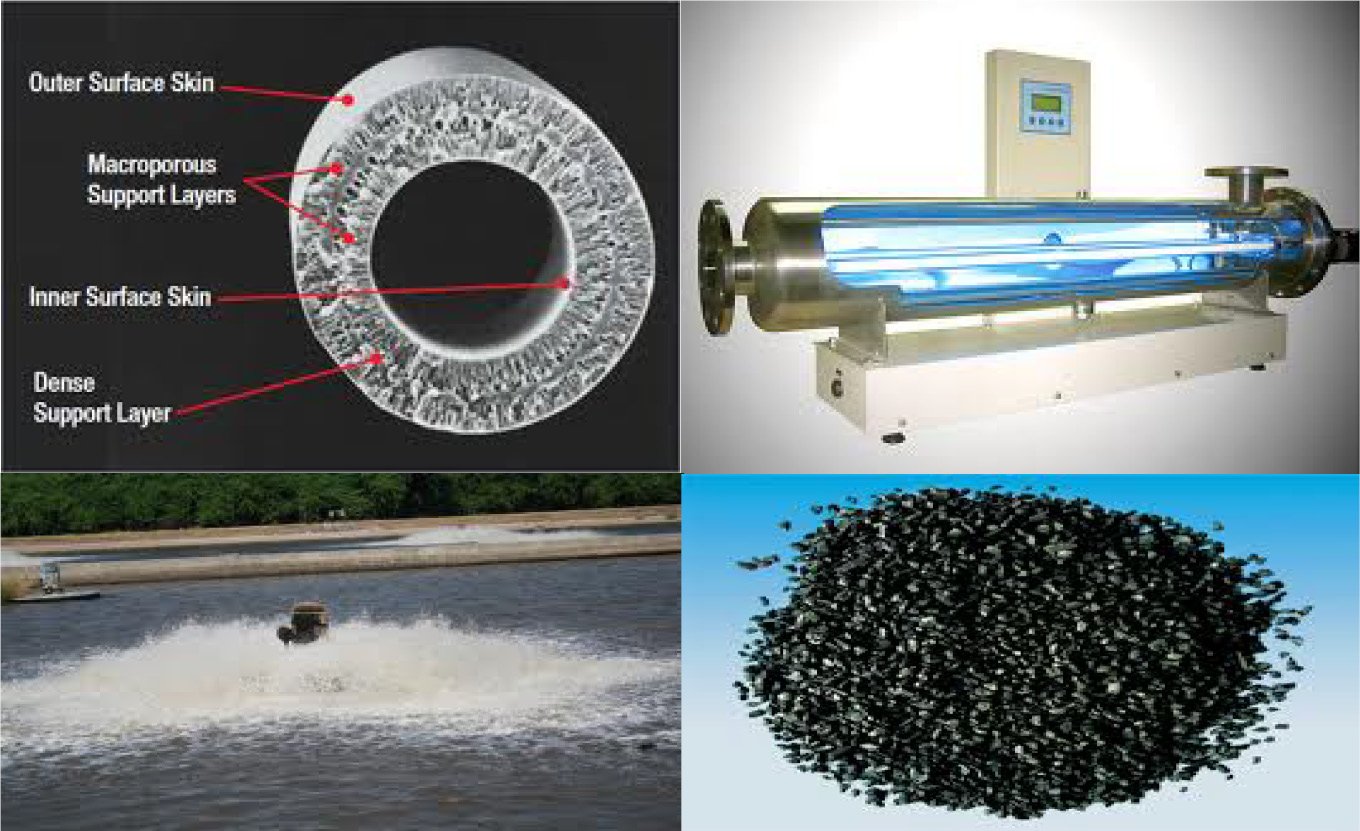
- Granulated Activated Carbon
- Distillation
- Ozonation
- KDF Resin
- Solid Carbon Block
- Water Boiling

Each of these filtration, purification, and/or sterilization processes can be effective to some degree and have a place for use in particular circumstances. Some of the methods remove bacteria, some also virus’s and some chemicals and pesticides.
When assessing the effectiveness of each of the processes, many considerations need to be assessed. This includes;
- Flow rate of the water through the process (for example, in the ionization process, is there sufficient electrical polarisation happening,
- Chemical concentrations required to destroy bacteria and cysts,
- Light penetration of the technology into the water, for example, for UV purification, does the UV penetrate all the water passing by and for sufficient time.
Water Guidelines and Standards
There are several global organizations and governmental organizations that provide both guidelines and legally enforceable standards regarding water quality and safety. In some countries that are part of the health, others part of the Environment and some completely separate organizations.
All these organizations and governmental organizations have a common agenda of making water safe. They do this by predominately by setting the maximum level of a contaminant, including bacteria, viruses, metals, chemicals, radiological hazards, toxic chemicals, infectious agents, pesticides, herbicides to ensure that the water we drink, swim, and bathe in to be safe. Some of the higher-profile heath water agencies include;






World Health Organisation
World Health Organisation (WHO) Is a United Nations Organization that oversees and manages the UN policies and guidelines concerning any health-related matter, and this includes water.

Environmental Protection Agency
Water Regulations and Guidelines
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
WHO Water Guidelines
The WHO Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality is a very comprehensive 668-page document covering areas of water quality targets, management plans, Risk Assessments, Audits, Surveillance, Planning, Affordability, Sanitations, Desalination, Water Harvesting.
About Water
Commonly referred to as H20, Aqua, goldern liquid is one of the most important ingredients to the human race, with the body made up of up to 78%. The globe is covered by over 76% of the water, of which only 12% is drinkable. It can exist in gas, liquid, ubiquitous and solid forms. Water is the only common substance found in these states naturally. Water is colorless, odorless, and tasteless.
One of the attributes to water is that substances can be dissolved in water (such as minerals), bacteria can grow in water, fish can live in water. Because of this attribute, water is very rarely pure. For humans, pure water is not as ideal as we require mineral and XXX to be included to stay healthy.
The water molecule is very small, measuring only 0.278 Nanometers (0.278 x10-9 m or .000278 x 10-6m or 0.000278 microns)
Molecular Structure
A water molecule consists of two hydrogen and one oxygen atoms weighing 18g/molecule. They are polar covalently bonded together, forming a V-shaped molecule. Water molecules are typically symmetric. Each molecule has a slightly more positive and slightly more negative side.
This is because the water molecules are polar covalently bonded, which is share electrons unequally. Other non-water polar molecules can surround the water molecule.
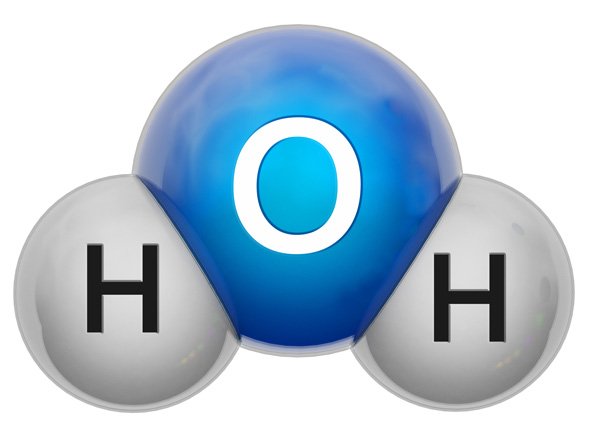
One interesting fact about water is that unlike many substances, when water is at 4C or less, water stars to expand, meaning that density is less in a frozen state. When water is referred to as hard water, it often means that it contains a higher than average concentration of minerals.
Some of the minerals could be magnesium and calcium.
The water molecule is one of the smallest and lightest around. The compound is simple, with common reactive elements, yet one of the most amazing substances known. Behind Hydrogen H2, Water H2O is the most common molecule.
When in a liquid form, the atoms in water move between other atoms. The atoms are continuously changing due to a process called protonation/deprotonation, staying less than one millisecond.
Spectrum
The graph below shows the size of the molecules when we look at water characteristics.
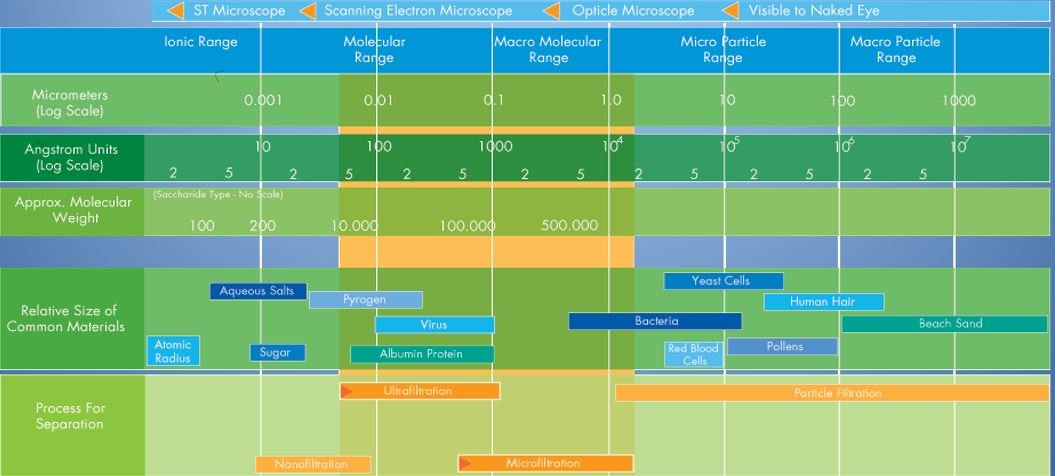
Micro-Filtration
Microfiltration refers to the process to removes any elements larger than 0.1 to 10 microns (micrometer- m). There are membranes that allow molecules either in a gas or gas form smaller than this to pass through the microscopic membrane. The microfiltration process is fundamentally the same as reverse osmosis. Microfiltration removes all bacteria, protozoa’s, Giardia, and Cryptosporidium.
Ultra Filtration
Ultrafiltration refers to the process to removes any elements larger than 0.005 to 0.10 microns (micrometer- m). Some membranes allow molecules either in a gas or gas form smaller than this to pass through the microscopic membrane. The ultrafiltration process is fundamentally the same as reverse osmosis. Ultrafiltration not only filters out what Micro Filtration but as well as viruses.
Nano Filtration
Nanofiltration refers to the process to removes any elements larger than 0.001 to 0.005 microns (micrometer- m). Some membranes allow molecules either in a gas or gas form smaller than this to pass through the microscopic membrane. The nanofiltration process is fundamentally the same as reverse osmosis.
Nanofiltration removes everything ultra filtration plus many nutrient, pesticides, and herbicides. It can remove salts from water, desalination. The process also removes solutes. The filtered water is extremely low of any nutrients below WHO standard guidelines. Nanofiltration only practically operates under high water pressure.
Electrochemical
The electrochemical water purification process refers to when water acts like a conductor when water is between two different elements with different and opposing electrical properties. The water allows charge to be transferred between the two elements, and a spontaneous electrical current is created. The technical term for the reaction is called an oxidation and reduction reaction, Redox. When an element loses electrons, it is called Oxidation, and when an element gains an electron, it is called reduction. When two elements are placed together with a transfer fluid, it is called an electrochemical cell.
As the electrical current passes through the water, the energy from the electrical charge destroys any live bacteria, oocysts, cysts, viruses, and anything else alive.
Many elements can be used to generate this voltaic cell (as opposed to the electrolytic cell where an external electrical supply is provided). These include carbon and zinc.
Electrodialysis
Using Electrodialysis in a water purification situation destroys germs, bacteria, and cysts through is the process of passing electrical energy through the water. It is accomplished by electro-deionization. It is primarily used for saltwater desalination.
Aeration
Aeration, as the name suggests, introduces air into the water, in particular oxygen. The oxygen metabolizes microorganisms, reduce carbon dioxide as well as it removes methane and hydrogen sulfide. It improves the smell of the water, making it good to drink.
Aeration is a particularly good where water has a high iron and manganese content, removing the bitter taste of the water. The Aeration process needs to be used in conjunction with another process to remove harmful bacteria, cysts, and viruses.
Iodine Disinfection
Iodine can be used as a water disinfectant, often referred to as water purification. The chemical iodine has the ability to destroy bacteria, viruses, and cysts at appropriate levels of concentration and sufficient time to contact the microorganisms. At low dosages, iodine is ineffective against Giardia and Cryptosporidium (see WHO guidelines). Iodine requires sufficient contact time with bacteria, viruses, and cysts to destroy. Short contact with iodine may be in effect.
People with thyroid disorders or pregnant women should not use Iodine in water as it has a significant impact. In addition, no one should have more than 5 mg of iodine per week. That’s less than five drops of un-concentrated iodine.
Chlorine Disinfection
Chlorine disinfection refers to the process where chlorine is added into the water with the view of killing bacteria, viruses, protozoa cysts like Giardia and Cryptosporidium. Chlorine is an oxidization agent. The chlorine at drinkable levels destroys harmful bacteria but not Giardia and Cryptosporidium cysts.
Chlorine can react to naturally occurring chemicals creating harmful by-products such as chloramine (a dangerous carcinogen).
Often Chlorine is used in conjunction with other chemicals to avoid this carcinogen. Chlorine Dioxide can be used in conjunction to prevent this reaction from occurring.
Chlorine Dioxide Disinfection
Chlorine Dioxide, CIO2, has been used for over 100 years to disinfect water. By adding Chlorine Dioxide, a biocide, in water it becomes an oxidant. The by-product of this is chlorite. As an oxidant, it is able to destroy bacteria and cysts. It is often used to improve the taste of water, reduce iron and manganese, and hydrogen sulfide compounds.
There are some low levels of adverse impacts on human health, such as neurotoxicity and reproductive toxicity.
Ultra Violet light
When water is exposed to sunlight, it has powerful purification qualities. It is able to eliminate bacteria, microorganisms, cysts, germs, and viruses through a natural process. This process has been around for day one and has been proved effective. It is a natural disinfectant.
The Ultra Violet radiation (UV radiation) of sunlight is the practical disinfection component. The UV wavelength that is most effective in destroying germs is at 254 nanometres. The UV radiation can be simulated by non-natural means.
For UV water purification to be effective, the UV rays need to have the right combination of the length of time, energy levels, and contact to destroy dangerous organisms and germs.
Reverse Osmosis
The reverse osmosis process refers to passing a fluid through a membrane by applying pressure (hydraulic pressure) to remove unwanted material. Reverse osmosis is usually used with clear water. When used in conjunction with water and the appropriate size membrane, it is able to effectively remove bacteria, viruses, cysts, giardia, and cryptosporidium.
It is one of the most used processes to filter/purify water and is used in municipal water plants, commercial buildings, homes as well by the Sure Aquaproduct group.
Forward Osmosis
The forward osmosis process refers to passing a fluid through a membrane without applying pressure (except atmospheric pressure, natural forces) to remove unwanted material. When used in conjunction with water and the appropriate size membrane, it is able to effectively remove bacteria, viruses, cysts, toxins, giardia, and cryptosporidium.
Forward osmosis is used in conjunction with some solute. The solute material is nominally a sugar-based. Forward osmosis is exceptionally effective to be used to purify and range of liquids including saltwater, urine and brackish water.
The drawbacks of this forward osmosis are
- It is very slow to filter the water, and
- The filtered water may not be suitable for a person with diabetes due to the added sugars
Activated Carbon- Granulated
Activated Carbon is a natural material. It is derived from coal, charcoal, coconut shell, lignite. It is processed into form granules to make it exceptionally porous, creating an enormous surface area that allows either adsorption or chemical reactions. As little as 1 gram of granular activated carbon equates to a surface area of almost 2000 sq meters.
Depending on the sources of the activated carbon made (from where it has been derived), each will have slightly different performance characteristics. For example, bituminous carbon has a higher chlorine absorption, whereas coconut carbon improves the taste of water.
Activated Carbon can also be treated with a specific chemical to use the absorption qualities to destroy bacteria.
With the exceptional porous qualities of the granulated carbon, when water is strained through the granules, any chemicals in the water will “stick” to the carbon surface, making a small film. (Carbon absorption process). This is effective in removing chlorine, benzene, radon, toxaphene, and other natural and man-made compounds.
Water needs to be passed through the slow to allow the surface area to work effectively; otherwise, the efficiency may be as low as 0%.
Other issues with activated carbon are;
- Activated Carbon (no form) removes bacteria.
- Channeling may occur; that is, water makes a direct path through the granules.
Silver impregnated Granula Activated Carbon
Silver-based Granular Activated Carbon has a minute percentage of silver spray, typically 1-2% of the surface area. The silver is meant to stop bacterial growth.
As water is leached through the granules, the silver becomes prematurely removed into the water supplied.
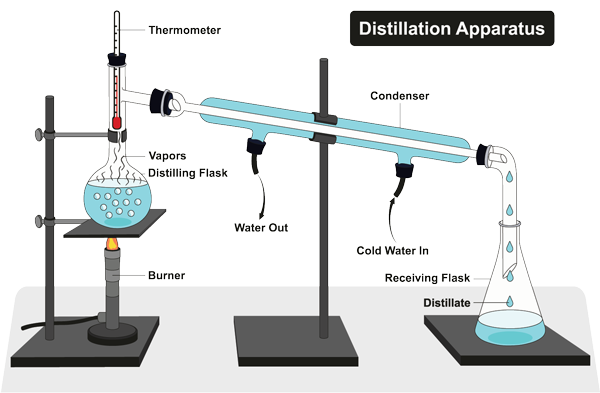
Distillation
Distillation is the process of heating water until its vapor point and then recondensing the steam into a container. The collected water has all the impurities removed. This water is called distilled water.
Distilled water has virtually no minerals. Humans require some minerals in water for dietary purposes to maintain proper health.
Ozonation
The ozonation process refers to when ozone, O3, is used to purifying water. It is one of the best ways to purify water. Ozone, O3, is an effective oxidizing agent, as it has a very high oxidation potential and has a ½ life of less than 30 minutes, making it very effective in making water pure, odorless, colorless, and safe. Any organisms, microorganisms, bacteria, oocysts, germs, viral DNA (such as smallpox, herpes, and hepatitis) and viral RNA (e.g., measles, mumps, West Nile, rubella, and influenza), heavy metals, and toxins cannot survive when in contact with ozone.
Ozone is a pollutant at ground level being created by hydrocarbons and nitrogens getting into contact with sunlight.
The ozonation process is typically used in large plants as it requires equipment and energy. It is typically used with a filtration system.
KDF Resin
KDF (Kinetic Degradation Fluxion) Resign is a brand name of a product that has been designed to filter water. It uses a copper and zinc alloys that, when water passes through, creates electrochemical oxidation, electrolysis, destroying bacteria. The process is known as “redox.” In this process, electrons are transmitted between molecules, and new elements are created. The old elements of harmful elements are eliminated. For example, chlorine is transformed into chloride. The heavy metals in the water are attracted to the KFD surface due to the electrical potential difference.
The KFD is usually used in conjunction with activated carbon (granular) to remove specific chemicals.
Ceramic Filters
Ceramic filters are a man-made product that is manufactured with a specific designed pores size to allow water filtration, typically 0.5 microns. Ceramic filters can be used in either a forward or reverse osmosis process.
Often silver is used in the ceramic to stop any fungicidal or algaecides or bactericidal growth. As silver is toxic to humans, silver levels must be kept to a minimum. All water filtration systems in the US must be registered with the EPA.
Solid Carbon Block
Solid Carbon Block absorbs viruses nor bacteria and destroying them with “food grade” pesticides or iodine. The pesticide or iodine s is saturated in the Carbon Block. The bacteria and viruses are attracted to the carbon block by “electro-attractive forces.”
Solid carbon blocks do not work well to destroy Protozoa’s cysts, such as Giardia and Cryptosporidium.
Water Boiling
Boiling is the most effective in removing bacteria, viruses, and the like out of water provided it is boiled at 100C for at least several minutes.
Comparative Rating of Filtration, purification, and Technologies
The below table provides some guidelines on how effective the technologies are for a portable device when traveling, camping, or required in a disaster or emergency. This assessment takes into the following parameters;
- Chemical
- Speed of access to water
- Portability
- Ease of use
- Bacteria removal
- Cysts removal
- Virus remove
Filtration Purification Method
Description
5 being the best
Water passes over the carbon with a slightly electro-positive charge











Final Say
In an economic and environmental climate that forces us to reconsider bottled water, Australian’s are fortunate enough to have the alternative of purchasing reusable bottles.
Australian water is said to be world standard drinking water, but you are encouraged to adopt the use of water filters.



