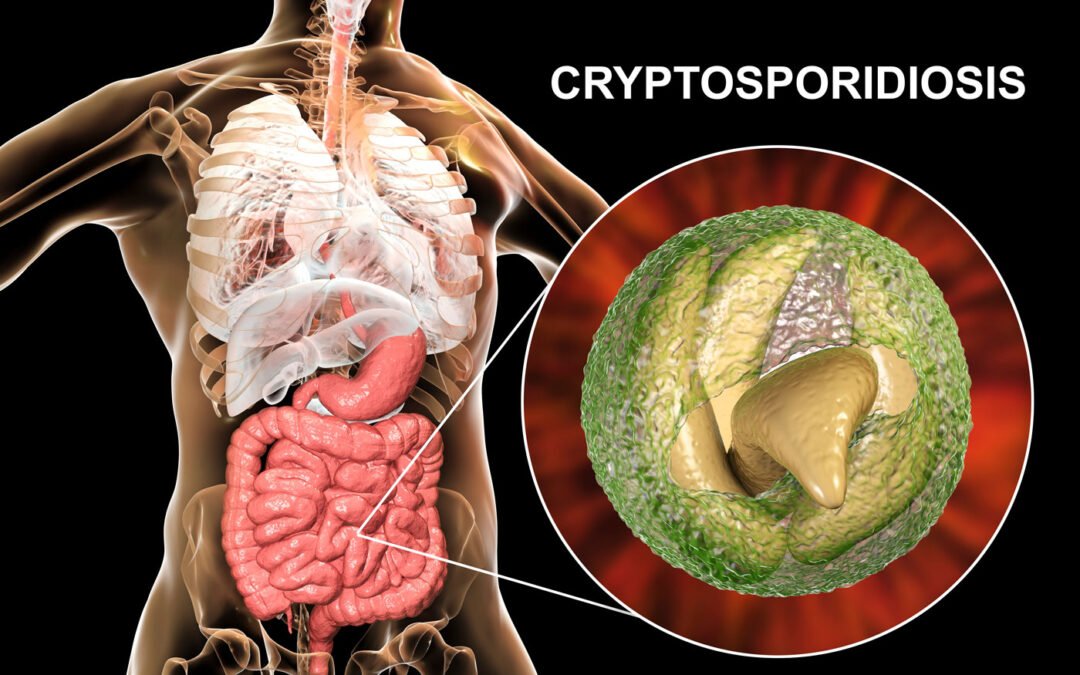
Cryptosporidiosis
Cryptosporidiosis
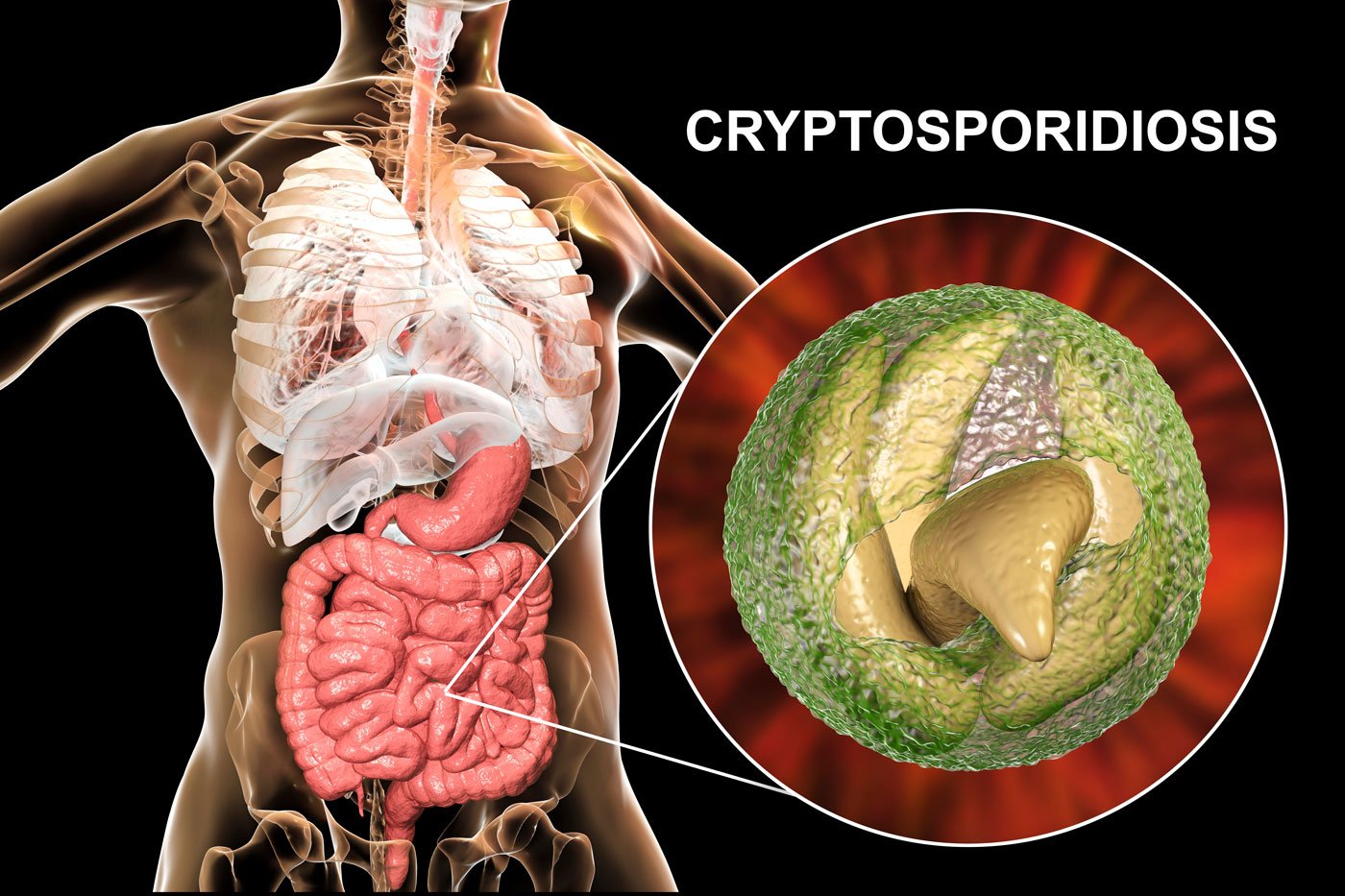
Cryptosporidiosis is a common illness caused by contact with a single-celled parasite called cryptosporidium. Although not discovered until 1976, cryptosporidiosis is one of the most common waterborne diseases. It can be fatal to those who are already in a vulnerable physical condition, such as pregnant women or anyone with HIV, AIDS, or cancer.
The most common symptom of cryptosporidiosis is watery diarrhea. However, some experience nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, and dehydration. Those with cryptosporidiosis usually experience symptoms between two and seven days after ingesting contaminated water. Symptoms typically last less than two weeks.
Diarrhoeal parasite spreads through contaminated water
Cryptosporidiosis can be found in any country but is more common in developing countries due to low-quality sanitation facilities and a lack of access to safe water. Cryptosporidiosis makes up 50.8% of parasitical waterborne diseases. In many developing countries, the rate of cryptosporidiosis is exceptionally high, making up 8-19% of all diarrheal diseases.
Unfortunately, there isn’t a failsafe way to treat cryptosporidiosis. The best one can do to drink lots of safe, clean water, replace electrolytes, and get plenty of rest. In severe cases, diarrhea medication and intravenous fluids can be used. However, this isn’t necessary for most people.
Final Say
The most reliable way to avoid cryptosporidiosis is to make sure you don’t ingest contaminated water from any source. Invest in a good water purification system that is failsafe against cryptosporidium and avoid swimming in unsanitary water.