Electrochemical Water Treatment
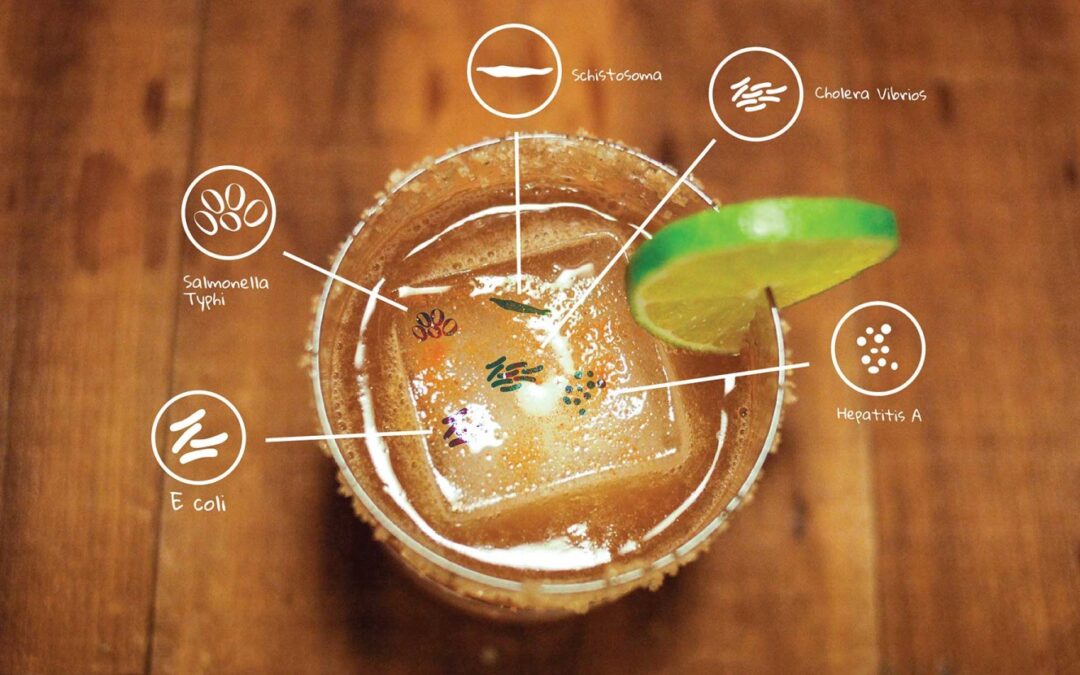
Electrochemical water treatment is a rare but highly effective way to produce clean and germ-free water. However, electrochemical products are currently scarce in the market because of the relative unfamiliarity to the technology as well as the enormous competition of other water treatment methods.
Basically, this type of disinfection is done by passing a current of electricity between electrodes (cathode and anode), resulting to changes in pH levels that in turn encourage pollutant desorption. The technique does not require addition of chemical compounds, but it is nevertheless the action of various chemical substances in the water that does the decontamination. Electrodes made from platinum group metals and their oxides are most suited for this type of process.
There are many reasons why electrochemical water disinfection has only been developed recently. Sufficiently stable electrodes have only been enhanced in the last forty years. Also, the practical interrelationships between chloride concentrations, electrolysis and water quality have been investigated methodically just in the previous decades. Lastly, only a few electrochemists had been engrossed in the topic which resulted to errors in device-making and irrational hypotheses to the mechanism of the process.
How Electrochemical Disinfection Works
The mechanism behind electrochemical disinfection is fairly simple. It is agreed that the cleansing of the water springs from desorption induced regeneration that affects the surface of porous carbons. Simply put, the electrical current allows chemicals to effectively react to microorganisms and kill them in the process.
The cathode, which is the reducing electrode, generates hydroxide ions that increase the alkalinity of the water around it. Through this, desorption of pollutants is promoted and they migrate to the anode for oxidation – hence their destruction.
Pros and Cons of Electrochemical Treatment
The advantages of this type of treatment are obvious. There is no need for the transport, storage and utilization of disinfectants which are otherwise needed for chemical methods of water treatment. The disinfection also has an inherent reservoir effect thereby marking cost-effectiveness and the need for less maintenance. Finally, there is no real need to induce power from an electrical supply grid as the principles of photovoltaic or solar energy can be used.
This is crucial to disinfect water in developing countries.
On the other hand, the major disadvantage comes with the mass transfer limitations between the electrodes. Residual pollutants could not be avoided and thus the cathode has to be cleaned after several cycles. If not, pore blockages and damage to adsorption sites decrease the regeneration efficiency. There is current research though that aims to develop adsorbents that are able to regenerate 100% of their capacity through electrochemical regeneration.
The Bottom Line
The use of electrolysis to chemically treat water has more advantages compared to other conventional techniques. This has been proven with its use in disinfecting drinking water, swimming pools, dental water supplies and industrial cooling water. Although this technology is not in full use today, the cost and performance advantages will eventually pan out to the wider use of electrochemical techniques in the future.