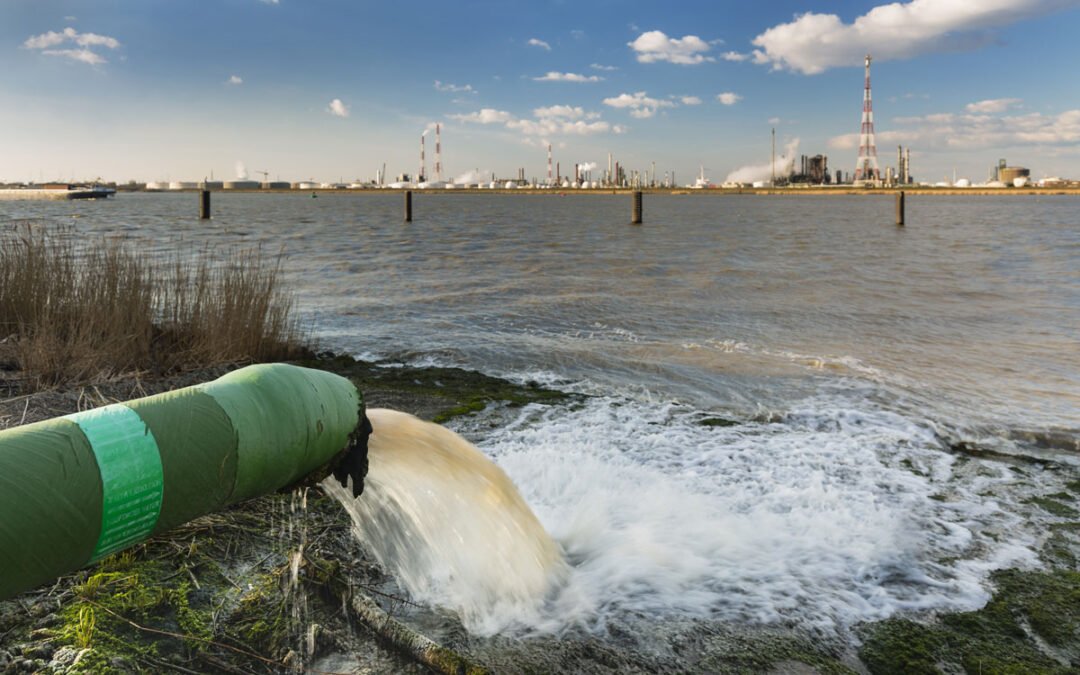
The Global Effects of Polluted Water
The Global Effects of Polluted Water
“Contaminated water supplies are killing more people daily than the 2020 Pandemic. It is the biggest health risk to all of mankind …threatening both quality of life and public health. It’s the biggest and most difficult crisis the world has to face.“
Even though drinking water quality may vary in different parts of the world, water pollution is a problem that all of us should be aware of. Water Pollution and contamination is an increasing topic of concern, and all the health risks involved should be well understood.
It is estimated that over 90% of all water ways is contaminated.

What exactly is contaminated water?
Water is said to be contaminated once pollutants are introduced to render it unsafe and unacceptable for human consumption, or unable to support human life. The contaminates can take several different forms, bacteria, chemicals, and pollutants.
A Worldwide Crisis
According to the Australian National Health and Research Council reports, there are too many examples that are directly contributing to drinking water pollution that cause an inexcusable adverse impact on human health. The most prevalent cause of widespread health risk associated with drinking water is contamination, either directly or indirectly, by human or animal excreta and the microorganisms contained in feces.”
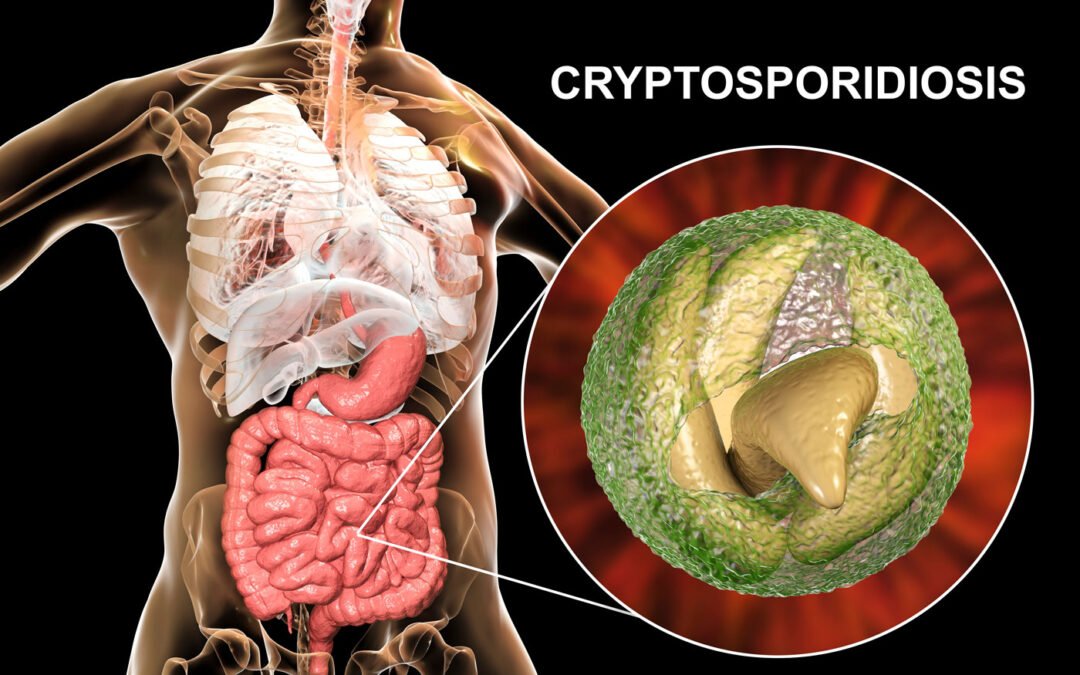
Pathogenic microorganisms in the water are the most significant risks to your health. Waterborne pathogens can cause outbreaks of illness in communities, in some cases causing death.
Dangers and Consequences
Pathogenic microorganisms are disease-producing microorganisms such as viruses, bacterial diseases, and parasitic worms.
What is a virus?
A virus is a microscopic parasite of plants, animals, and bacteria in well water that can cause disease.
Some of the more common viral infections affecting world water today are Gastroenteritis (cause of diarrhea), Hepatitis A, Polio, Dengue Fever, Salmonella infection, and dysentery.
What is a bacterial disease?
Bacteria are single-celled, microscopic organisms found in all environments. These environments include soil, water, and the bodies of animals and humans.
Some of the more common bacterial diseases affecting world water today are Cholera, E.coli, Dysentery, Salmonella, and Typhoid Fever.
What is a parasitic worm?
Parasitic worms are organisms that feed on their living host, using them as a source of nourishment and protection. Parasitic worms live in the intestines and other organs. They disrupt their hosts’ nutrient absorption, which causes disease and illness in humans. Some of the most common by parasitic worm related diseases affecting world water today are Guinea Worm Disease, Schistosomiasis, Enterokinases, Ascariasis, and Tapeworms.
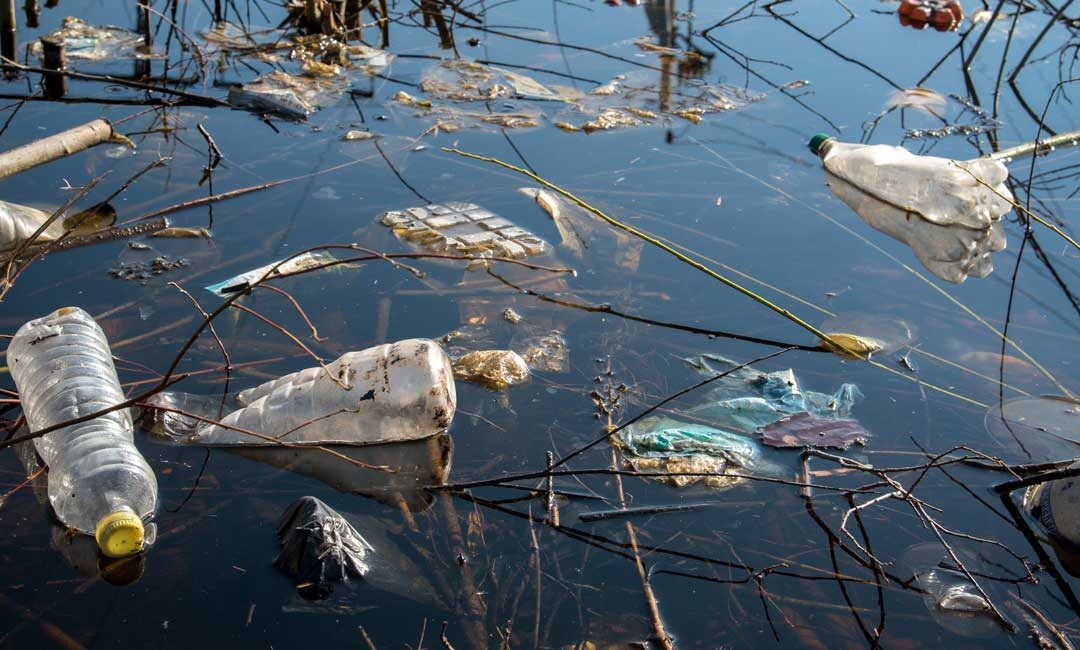
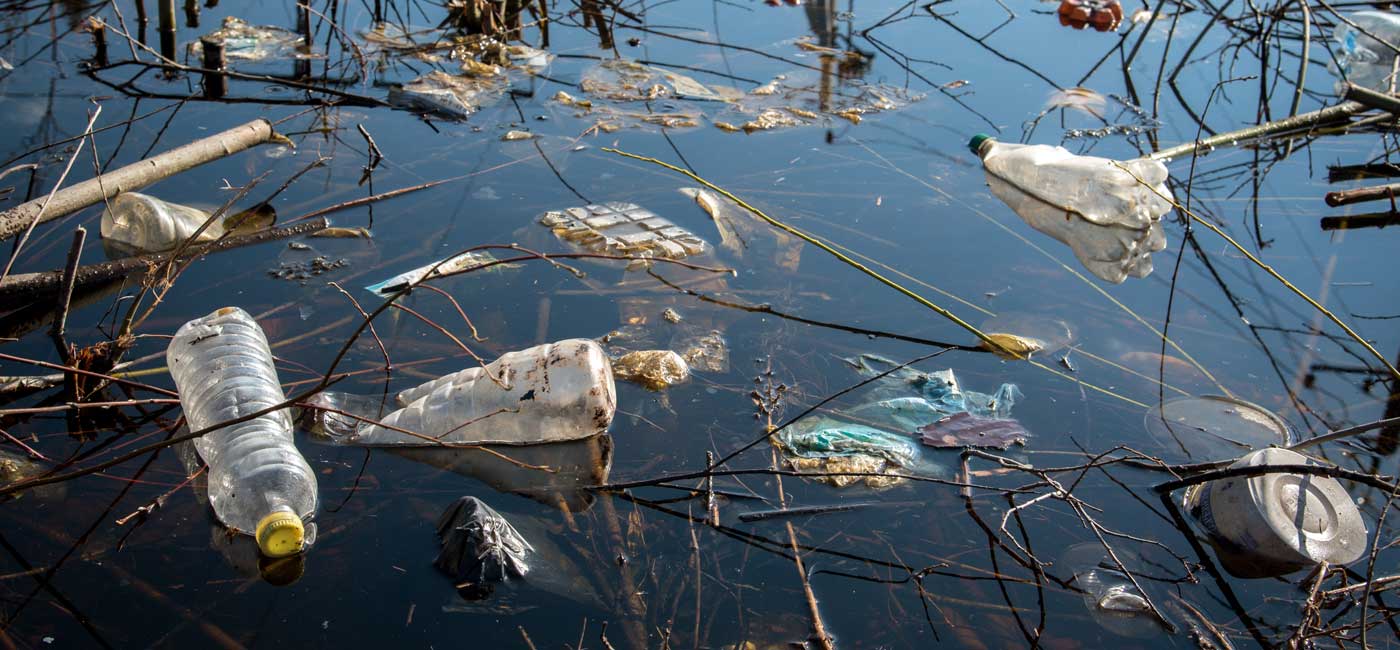
How are our waters polluted?
When it rains, the water picks up human and animal feces and harmful chemicals from the ground. These travel with the water and end up in rivers, lakes, and underground water supplies.
In most cases, water pollution begins at the water source. One source is above ground contamination known as Surface water contamination. The other is underground contaminants referred to groundwater.
Surface water contamination starts once the rain starts falling from the sky. The rainwater becomes contaminated from collecting air contaminates, known as acid rain, or collects pollutants in stormwater, pesticides from farming or gardens, or industrial waste. These all flow into rivers, lakes, and dams, our water source.
The groundwater, as the name implies, is from below the surface and retrieved wells or extracted from the ground for public water supplies. Groundwater can be polluted by contaminants that drain into the water source from; landfills and septic systems, careless disposal of hazardous products, chemicals used in farming and agriculture, and leaking underground storage tanks.
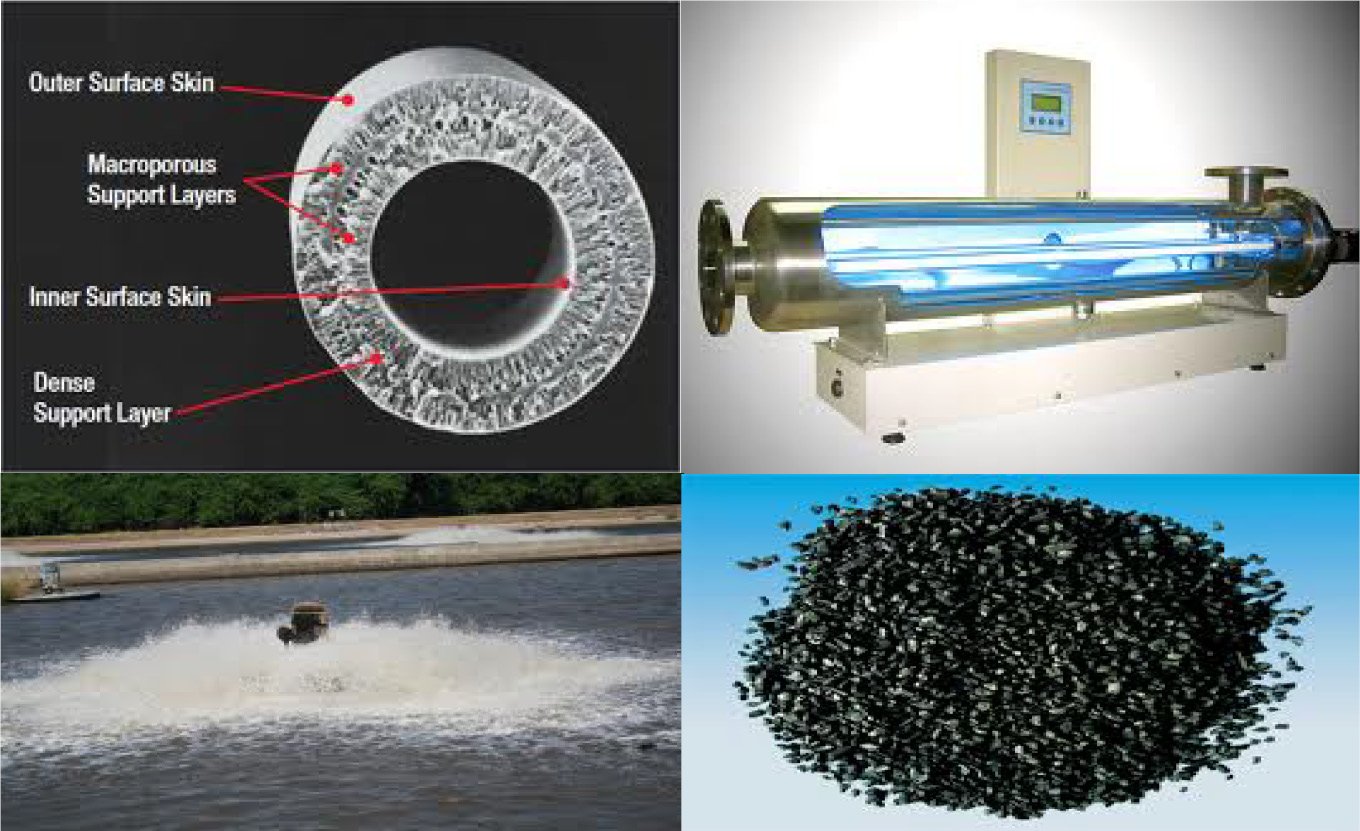
Virtually every water source for consumption on this planet is contaminated. Most developed countries decontaminated the water before providing for public use. The decontaminated water is processed through several modern water treatment techniques and extensive, large, and costly facilities.
However, this decontamination, in itself, introduces its own dangers. Often Strong chemicals are used in the water treatment process. These chemicals can be harmful when consumed over long periods.
According to the Global Healing Centre, some of the proven effects of long term exposure to strong chemicals in drinking water include brain damage, Alzheimer’s disease, dementia, and cancer.
Some of the most common chemicals affecting world water today are Fluoride, Chlorine, mercury, PCB’s (a man-made chemical), MTBE (contained in gasoline), Dioxin, HCB (hexachlorobenzene), DDT (an organochlorine insecticide).
In less developed countries where the toxic waste management is not as strict, toxic metals wastes are illegally dumped and allowed to leach into the water systems and supplies. The toxic metals include arsenic, barium, chromium, lead, mercury, and silver, and can cause acute poisoning and cancer, as well as other health effects.

Diarrhea – A Global Epidemic
The biggest world spread disaster of contaminated water is diarrhea.
The World Health Organization has pinpointed diarrhea as a prominent fatality, causing 4% of all deaths worldwide. There are over 4 billion cases of diarrhea worldwide every year and growing. In 2019, diarrhea was estimated to have killed over 3.2 million people. A large percentage are under the age of 5 years living in 3rd world countries.
In developed countries, it is also prevalent and should not be discounted by 2.3 deaths per 100,000 people in the US dying.
How an individual can help to Reduce Water Pollution
“…water pollution is a problem that all of us are aware of. It’s all around us, from the air we breathe to rubbish in our streets, to the waste from our factories, and to the exhaust from our cars. All this pollution eventually makes its way water sources, dams, lakes, and underground reserves. Water Pollution and its contamination must be a topic of concern for the community to business and community leaders. The health risks impact should be well understood.”
The world pollution and contaminants that leach into the water can be substantially reduced if everyone takes a little responsibility and action for their own contribution to pollution.
The leading cause of water pollution is the greenhouse gases created from the industry and the generation of power. China is the main culprit contributing over 30%, followed by a distant second in the US at 15%, then India at 7%. These three make over 50%. Australia contributes 1.07%.
Notwithstanding the above, every little bit counts. This is easier than most people may think. It all starts with taking precautions at home, traveling to work, and while doing leisure activities. Here are several small things you personally can undertake do help;
- Don’t litter, and be sure to recycle.
- Don’t throw chemicals, oils, paints, or medicines down the drain
- Use environmentally friendly household cleaning products
- Plant trees and plants around your home to improve the natural filtration process in the ground. This will stop nasty chemicals draining into natural water systems.
- Don’t overuse pesticides and fertilizers
- Reduce home power consumption by turning off lights, reduce heating levels, avoid air-conditioning
- Consolidate car travel, plan better use of the car
- Use public transport
- Reduce the unnecessary buying of products like excessive clothing (significant energy is required to produce them)

Almost any every day household activity can translate into water pollution. From the fertilizers in your garden to the oil from driveways, to paint and solvent residues from walls and decks, and even pet feces. When it rains, these are all washed into the stormwater sewage systems as well as rivers, streams, and lakes. These are all water sources where we get our drinking water from and how contaminated the source determines the quality of our drinking water.
Here are a few easy and essential steps in preventing water pollution around the home and daily life activities:
Have fewer hard surfaces
Hard surfaces such as asphalt and concrete don’t allow the water to seep into the ground. It reduces the runoff of your property into the stormwater systems.
Good alternatives to solid surfaces would be grass, gravel, deck wood, paving stones, or interlocking bricks. These all allow water to run into the soil. You can also control where the water on your roof flows by redirecting your gutters. It’s best to position them so that rainwater flows off into the garden where it can seep into the soil.
In the Garden
You should always use chemical-free, natural fertilizers like compost. It is easy to create your own compost at home by buying a compost bin. This helps keep waste from becoming landfill. Alternatively, you could use natural fertilizers, soil conditioners, or rotted manure. These will all help your soil retain moisture and keep your minimize your pollution.
Be sure not to overwater your garden. A large percentage of household water use and wastage is due to home irrigation systems. If your garden isn’t flat, try not to use an inefficient sprinkler system that doesn’t cover all areas of your garden. Try soaker hoses instead.
By having a simple rain gauge, you will know exactly how much water your garden is getting and will require. This way, you know not to water your garden if you don’t need to.
Overwatering gardens is one of the main reasons for chemicals draining from the soil and running into water systems.

Recycle Recycle -Throw Away Household Products Properly
Ideally, before you choose your everyday household products, you should be looking out for non-toxic alternatives. You can research products on your chosen supermarket website and take note of the environmentally friendly products.
Please make sure the waste products that they make their way into the recycling bin or whatever recycling program your city or town offers. The central concept is to avoid as much as possible to recycle everything possible to ensure that it does not reach to the rubbish tips. It will make a difference.
Reduce your energy consumption
One of the significant contributions to water pollution is energy generation, vehicle, household, and factory greenhouse emissions. Not only it pollutes our waterways, but it also is a significant contribution to global warming.
Every individual on the planet can reduce emissions. Below are a few small tips that will make a difference.
- Wear a jumper at home rather than turn up the household heating.
- In hot weather, increase the air-conditioning temperature a few degrees higher
- Plan your vehicle travels to be more fuel-efficient
- Keep your showers time to a minimal
- Turn power of completely from idle electronic equipment
- Turn off household lights when not in the room
- Use blinds to reduce heating of the home on hot days and heating loss on cold days

Educate Yourself
Lastly, go onto local government websites to find information on your local water situation. This way, you can know the risks you face and aim to make a difference in your community.
Be an activist in all the movements for better protection of our environment. With your support, laws will be made, and ultimately, the change will be made for the better of our planet