10 Ways to avoid dysentry on holidays
10 Ways to avoid Dysentry on holidays
It only takes the slightest drop of contaminated water to get dysentery!
Pick any one of the bacteria and virus from the table below. Each one has the potential.. They are not only found in third world countries. They are spread across the globe.
E coli, enterotoxigenic
E. coli, enteroaggregative
E. coli, enteroinvasive
Salmonella spp
Campylobacter jejuni
Vibrio parahemolyticus,
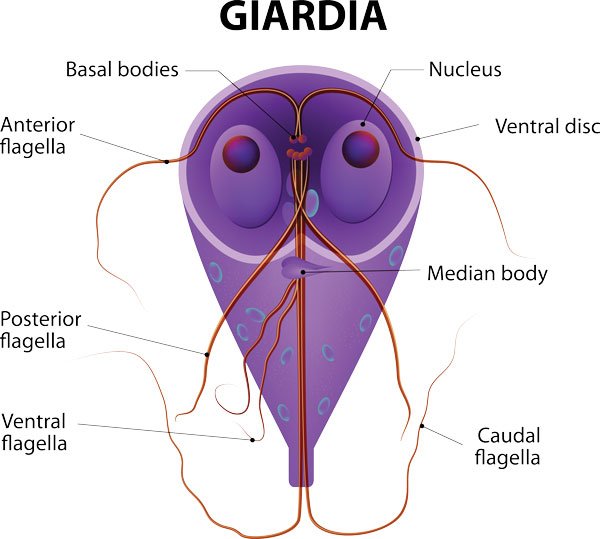
Giardia lamblia
Entamoeba histolytica
Cryptosporidium sp
Rotavirus
Norwalk virus
Did you know that approximately 1 in 4 people who travel for over a week will become ill (some studies show even higher) due to contaminated water?

In 2019 over 10 million documented people contracted some form of dysentery while camping or traveling. In some cases, it is mild though 1 in 7.3 people lose at least 1 day of their holidays, and 1 in 2117 are hospitalized.
These statistics are a little frightening and avoidable with a little precaution. Find out more later in this article.
What is dysentry?
Dysentery impacts the body’s digestive systems caused by directly related to drinking contaminated water or eating contaminated food. The symptoms include
Diarrhea. could contain mucus and blood in the feces
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Fever
- Dyhydration
- Dizziness
There are two main types of dysentery;Bacterial dysentery– it can originate the bacteria types Campylobacter, Salmonella, Shigella, enterohemorrhagic E. coli, to name a few. There are over 500,000 cases Trusted Source diagnosed in the United States each year.
Amebic dysentery is an intestinal infection caused by a parasite.
Dysentery should not be taken lightly. It can be fatal. It does have long term impacts on the human body including;

Some interesting facts to ponder about drinking water quality
We often take drinking water for granted. There are some alarming facts and government and authority behaviors that, to say the least, interesting. Read and be amazed
- In the US, more than 45% of bottled water is just tap water. FDA approves the process when sold in the State that it is bottled
- Even in “so-called” developed worlds, an estimated 46% of catchment water has unacceptable levels of Giardia and Cryptosporidium.
- All countries around the world have significantly reported numbers of Giardia, Cryptosporidium, and Gastroenteritis outbreaks. Over 20 million holiday days are being lost per year due to water-related illnesses.
- Many of the filters still let unacceptable levels of Giardia and Cryptosporidium through to the consumer. Filters should remove anything larger than 1 micron (US CDC recommendation) as giardia, and Cryptosporidium cysts can be that small as well as harmful bacteria.
- Most, more than 80%, ‘so-called’ freshwater streams in remote regions are unsuitable for drinking due to the contamination of giardia or cryptosporidium via animal droppings upstream.
- Bottled water is not necessarily bacteria-free. It is dependent on the bottling process.
The naked eye cannot see bacteria, cysts, and viruses in water. They appear invisible. You need to have laboratory equipment to identify waterborne bacteria and cysts
How to avoiding dysentery – water-related Illnesses
We have listed 10 ways to avoid dysentery and Gastroenteritis. Taking these simple precautions can and will significantly reduce the risk of becoming ill from contaminated water.
1. Avoid drinking tap water
In most countries, including developed nations, drinking water quality is very suspectable and questionable at best. There are regular outbreaks of giardia and cryptosporidium in most countries.
When you live in a particular environment for long enough, your body adapts. With reference to water intake, their digestive systems build immunity to certain strains of bacteria and cysts in the water.
Even though this may be the case, where hygiene is poor or nonexistent, the number of Giardia, Cryptosporidium, and Gastroenteritis outbreaks is significantly prominent. This particularly prevalent in the third world where hygiene levels in low.
For people traveling from a developed country, it is common, one in five people will be adversely affected by water no matter what country they live in. This is due to the digestive systems as the immunity system is not as developed and prone to adverse effects. For this reason, people from developed countries are significantly more prone to dysentery. Some statistics stating its one in two people are affected.
In the US, in 2019, some 46% of tested water supplies exceeded America’s water governing limits on safe water. ( Levels of Giardia, Cryptosporidium or Gastroenteritis related bacteria). In France, the statistic is 37%, Nigeria 67%, South Africa 58%, and so it goes on.
Each of these countries has elaborated water cleansing plants, including filtration and chemical disinfectants, to purify water for consumption.

It does not take much for these bacteria, and viruses enter into the system post this cleansing process.
It is advised to be very careful of drinking tap water in especially when traveling. The probability that increases significantly in getting sick is very high.
There are several methods to kill or remove bacteria, cysts, and viruses, such as boiling the water, adding chemicals, or filtering. Remember, the filter to be effective should be at least 0.5 microns. SureAqua products remove 99.9999% of bacteria and 99.99% of viruses, using its membrane technology.
2. Avoid drinking Bottled water ?
Just because it’s in a bottle doesn’t mean it is free of bacteria and viruses. All it means is that you have paid for the water and purchased another plastic bottle.
In many countries around the world, there is little to no regulatory standards regarding the quality of water being bottled. In the US, for example, it is legal (FDA approved) to sell tap water.
In third world countries, the bottled water industry is very unscrupulous and uses many unethical and immoral practices to sell water. This includes recycling water, using un-cleaned water bottles and filling it with plain tap water, and re-sealing the caps.

There are many brands that supply spring water, mountain freshwater, glacial water, etc. It should be noted that the water from these sources is just as likely to be contaminated as any other water source. Studies have identified that there are often high levels of chemicals, Giardia, Cryptosporidium. This causes gastroenteritis because of the bacteria that enter your digestive systems.
Picture this, a company taking water from a stream in the mountains. It portrays is as healthy and clean. If the camera moves up, you see that there is a farm upstream with cattle or some other farm that uses fertilizers. One of the main spreaders of bacteria is birds. They are somewhat immune to the bad bacteria. Ther feces are spread wherever they fly. From here, local animals eat these feces, and their feces end up in the water system. It results in an incredibly high percentage of animals having Giardia and Cryptosporidium cysts in the digestive systems. Their feces all eventually end up in our water systems.
There are many reputable water manufacturers that filter and or purify the water to remove bacteria effectively. Because it is such a big industry and not well regulated, there are an element of some manufactures taking short cuts.
Studies have shown that where what appeared to be bacteria-free water in bottled water during the manufacturing process, bacteria can come out of a ‘hibernation’ after some time in certain conditions. This prone to happen when bottled water is stored for many months in hot conditions before use. This appears to activated the growth of bacteria.
Are you willing to take the risk?
3. Only eat peeled fruit
Most fruit is our society has been sprayed with insecticide, washed with water to remove it before it reached consumers. The source of the water, in many instances, may not have been filtered or purified. There is every chance that there is bacterial growth on the surface of the fruit.
Even though the fruit may be dry when you receive it, it would be best if you are not able to wash it thooughly to peel the fruit before eating it.
Another option only to eat fruit that you can peel.

4. Avoid eating uncooked salads such as green salads and the like
When you are traveling to countries where hygeniw standards are not high, it is suggested when you eat at out in restaurants, avoid ordering uncooked side salads. The salads usually are typically washed under tap water. Even if they said they say, they wash their salads in bottled water, see what we say about bottled water earlier in this article.
Play it safe by only eating cooked food.
Should you have severe cravings for salads, purchase your vegetables, then you are in control of cleaning them correctly.
5. Avoid poor hygiene
Having good personal hygiene is paramount when traveling. The risk of getting dysentery significantly increases with poor hygiene. Dysentery can spread like wildfire in a group. It only takes one person in a group to have poor hygiene to cause an outbreak. It is very common when one person in a traveling group that many people in the group will also fall ill because of not taking precautions.
Some tips include for good hygiene include;
- Avoid placing your hands in your mouth
- Avoid place objects in your mouth
- Wash your hands thoroughly, including between your fingers, back of hands, and your wrists.
- When using public toilets, thoroughly wash your hands after going to the toilet.
- When you leave the bathroom, use some paper towel to open and close the door, as the previous person may not have washed their hands.
- Always wash your hands thoroughly before meals
- Cutlery should be wiped with some disinfection wipes.
6. Avoid using hotel tap water to clean teeth
Many of the top-end 5-star hotels have integrated water filtration and purification plant into their water supply. This is a costly exercise and needs constant monitoring to ensure a constant supply of filtered/purified water. The 5-star hotels can afford to maintain it, whereas lower-cost hotels don’t have the capability.
If you are not staying in a 5-star hotel, either use reputable bottled water or pre-boiled the water for use.
Coming soon is the SureAquaTap connection, which will, as the name suggests, connect directly to the tap and filter for immediate use.
7. Avoid having ice in alcoholic drinks
Did you know that bacteria can survive being frozen?
Ice in drinks can easily carry bacteria that can cause your illness. Waterborne bacteria and cysts can survive water temperatures from minus 40⁰ degrees to plus 60⁰ degrees Celsius.
8 Avoid opening your mouth in the shower
It only takes a drop of contaminated water to get sick. One of the places where you can get sick is from the shower, with water accidentally going into your mouth. Since the water in showers usually is hot, bacteria might be less likely to survive. The risk is relatively low compared to other ways of catching illness through the water.
9 Do not rely on iodine or chlorine tablets to effectively remove bacteria from your water.
The US Army has published a paper indicating that standard iodine or chlorine tablets are ineffective against Cryptosporidium and Giardia cysts. They state that the levels of chlorine or iodine need to be a level that makes the water undrinkable.
Secondly, there is a large school of thought, even should the iodine or chlorine that can kill the bacteria and cysts need to be in the water for some time. Suggestions the chemicals should be in the water for a couple of hours. This makes it unpractical in many circumstances.
Furthermore, the use of chemicals can be detrimental for people with thyroid conditions, young children’s growth, and pregnant women.
10 Avoid drinking locally made soft drinks or local beer and where there are known water problems.
Beer and soft drinks are predominantly water-based with added ingredients. In many manufacturing processes, the water is not treated to remove undesirable bacteria or cysts. In countries where the water quality is recognized as poor, there is potential the soft drink or alcohol to contain bacteria.
Only drink well known soft drinks and beer from countries where you know the water has been treated adequately.